How to Compare Independent Accountability Mechanisms on the Console
To support communities through the complaint process and as an ongoing knowledge sharing effort, the Accountability Console hosts information on all IAMs in a searchable database that links to complaints filed, IAM policy documents, projects about which complaints are filed, and other relevant information that communities and their advocates can use.
Communities harmed by internationally financed projects often face limited resources and access to information when attempting to seek remedy for that harm. Project affected communities often have very limited information about projects themselves, let alone where and how and to whom to raise concerns. Even when communities become aware of the existence of Independent Accountability Mechanisms (IAMs), the processes for successfully navigating them can be extremely difficult, as detailed in our Eligibility Bottleneck article. To support communities through the complaint process and as an ongoing knowledge sharing effort, the Accountability Console hosts information on all IAMs in a searchable database that links to complaints filed, IAM policy documents, projects about which complaints are filed, and other relevant information that communities and their advocates can use.
Viewing IAM Information on the Console
Though the focus of the Accountability Console is on complaints filed to IAMs, we also have a great deal of information on the IAMs themselves. The “All IAMs” list in the “Accountability” sidebar displays all 27 mechanisms for which we have data. This list includes some IAMs that have yet to report any complaints, like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank’s Compliance, Effectiveness, and Integrity Unit. There are also mechanisms that have since been closed or merged into other institutions like the EBRD’s Project Complaint Mechanism and Independent Resource Mechanism, which have become the Independent Project Accountability Mechanism. Clicking any of the IAM names takes you to that IAM’s dedicated page.
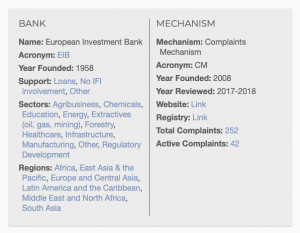
Mechanism and Bank Information
The gray box at the top of the page displays high-level information about the mechanism and its related financial institution(s). On the left side are the details of the mechanism’s associated bank(s), including the year it was founded, the type of financial support it offers, the sectors of projects, and the regions where the mechanism operates (though this only includes information related to complaints which have been filed, rather than the full project portfolio of the financial institution). Clicking any value in any of these sections will lead to a list of complaints with that support type, sector, or region. On the right ride is information about the mechanism itself, including its acronym, the year it was founded, the year of its most recent policy review, a link to its website, and a link to the mechanism’s public case registry, when available. Below this are links to all the complaints filed to that mechanism, and currently active complaints.
Charts and Analysis
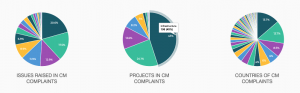
Below the info box is a short description of the mechanism (usually pulled directly from their website), followed by three pie charts detailing the following:
- The issues raised in complaints filed to that mechanism
- The frequency of project sectors related to complaints filed to that mechanism
- The countries where complaints were filed to that mechanism
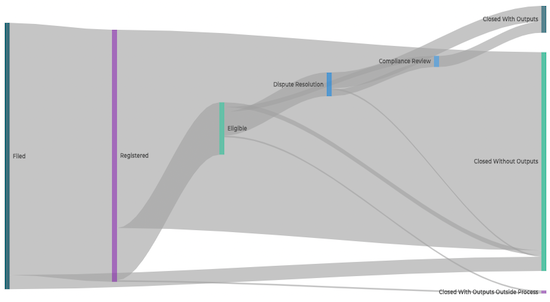
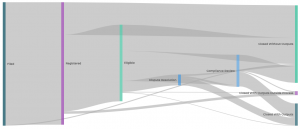
Following the pie charts is a flow chart which shows how complaints have historically been handled by that mechanism, including how many complaints have been filed, registered, found eligible, and undergone any substantive stages like dispute resolution or compliance review.
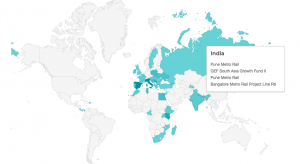
The global map represented below the charts allows users to view all complaints filed to that mechanism by country. Clicking on any country will open a list of all complaints filed in that country, and clicking a complaint will take you to that complaint’s dedicated page.
Documents
Any documents related to the IAM itself (policies, reviews, annual reports, etc) are presented in the Documents section. These documents are also accessible through our DocSearch feature, where you can search the content of any document in our database.
Policy Benchmarks
Logged in users can also see a list of almost 200 “policy benchmarks” that relate to the mechanism’s transparency, accessibility, and accountability. The list can be filtered by category, using the dropdown menu in the top right corner of the benchmark table. Clicking any benchmark value leads to a page with more information on that particular policy, citations from the mechanism or bank’s internal policy documentation, and a comparison with similar policies of all other mechanisms. Benchmark policies can also be compared directly with another mechanism, or organized in a customizable benchmark report, which has been described in detail here.

Understanding how different IAMs operate, where they operate, and what results one can expect from them, are critical components for improving the accessibility of these mechanisms for communities, and for informing advocacy of best practices for IAMs. The IAM pages on the Console provide one way to do this, though much more still needs to be done.
This article was originally published in the Accountability Console Newsletter, where AC’s Research team shares research and insights from the world’s most comprehensive database of Independent Accountability Mechanism (IAM) complaints, the Accountability Console. Click here if you would like to subscribe to the monthly Console Newsletter.

